Food stamps, SNAP, and EBT are terms that are often used interchangeably. But what are the more detailed differences between these terms? And why does it matter which one you use or hear?
Let’s explore how SNAP vs EBT differ – and why knowing the distinction can help you better access the support you need.
1. SNAP vs Food Stamps: What Changed?
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) is a well-known federal program in the U.S that helps low-income individuals and families buy food. SNAP was once widely known as “food stamps”, and many Americans now still casually refer to it as food stamps.
Initially launched as the Food Stamp Program in the mid-20th century, the program was developed to help low-income individuals and families buy groceries. For most of its history, the benefit came in paper stamps or coupons; recipients would receive these and use them directly at grocery stores to purchase eligible food items.
This paper-based system began to phase out in the late 1990s, as states adopted Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT) systems. EBT allows monthly SNAP benefits to be automatically deposited into recipients’ accounts, which can be used to buy food at approved retailers.
In 2008, the Farm Bill officially renamed the Food Stamp Program to the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP). The revised name emphasizes assistance and nutrition, distancing the program from the outdated imagery of paper “food stamps.” However, “food stamps” is a shorthand term people recognize nowadays.

>>> Also read: Restaurants That Accept EBT: Where To Use EBT At Restaurants
2. SNAP vs EBT: Is SNAP the Same as EBT?
Is SNAP and EBT the same thing? No, though the terms are often used interchangeably in everyday conversation.
SNAP is the federal assistance program that provides benefits to help low-income families afford food. And EBT is the electronic system used to access and spend those benefits.
As the largest program in the USDA’s nutrition portfolio and a critical part of the nation’s social safety net, it helps millions of low-income individuals and households afford nutritious food.
EBT, or Electronic Benefits Transfer, is the system through which SNAP benefits are distributed and accessed. It is a delivery mechanism – a secure and standardized way for participants to receive and use their SNAP benefits.
EBT functions much like a debit card. SNAP funds are electronically loaded onto a participant’s EBT card each month. You can use this card at approved retailers to buy eligible food items. When a purchase is made, the amount is deducted from the recipient’s SNAP account, and the retailer is reimbursed.
Recipients can use their EBT cards to buy many food items, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy. EBT cards are accepted at a wide range of stores across the U.S. You can use EBT at Walmart, Whole Foods, Trader Joe’s, and more.
These days, there is constant discussion about what items should or should not be eligible for purchase with SNAP benefits via EBT. For example, some states, like Nebraska, have introduced legislation to restrict the use of SNAP benefits for purchasing soda, reflecting a broader effort to promote healthier food choices among low-income households.

3. What’s the Difference Between SNAP EBT and Cash EBT?
Because EBT is a technical infrastructure, it can also be adapted to deliver other types of benefits, such as Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF).
You can only use SNAP EBT to purchase eligible food items and non-alcoholic beverages. SNAP benefits cannot be used to buy items like alcohol, tobacco, vitamins, pet food, cleaning supplies, or hygiene products.
Cash EBT is also administered through the EBT system. One of the common sources of cash benefits is TANF. Cash EBT can be used for various basic needs, including rent, utilities, clothing, transportation, personal hygiene products, or food from establishments that don’t accept SNAP. Funds can normally be withdrawn as cash from ATMs or used like a regular debit card in stores.
Both of these benefits operate through the same electronic card system. SNAP EBT is used only to buy food, while Cash EBT provides cash assistance for broader expenses.
>> Check more: When Does EBT Reload? Find Out When Your SNAP Benefits Arrive
4. How SNAP Works: Eligibility, Benefits, and Limits
Eligibility for SNAP is primarily based on household income, expenses, and other qualifying factors. In addition to income, citizenship status plays a crucial role in determining eligibility.
Applicants must be U.S. citizens or certain lawfully present non-citizens. Some non-citizens may face additional requirements, such as a waiting period before they can receive benefits.
To apply for SNAP, individuals should contact their local SNAP office or apply online through their state’s SNAP application portal. During the application process, they may need to provide documentation to verify income and expenses.
SNAP benefits supplement a household’s food budget, helping them purchase eligible groceries each month. The amount a household receives depends on its size, income, and allowable deductions.
5. More Benefits You Can Get with SNAP, EBT, for Free!
We want to let you know that SNAP benefits can help you qualify for several valuable programs and resources. One of the most helpful is the Lifeline program, which offers discounts to reduce your monthly phone or internet bills, and you can even receive a free device when applying for Lifeline through a popular provider like AirTalk Wireless.
Step 1: Visit the AirTalk Wireless homepage. Enter your ZIP code.
Step 2: Select a Lifeline Plan. AirTalk offers multiple options, such as Standard, Plus, Premium, and Unlimited.
Each plan caters to different usage needs. So make sure you consider the best one for you.
Step 3: Choose a discounted or free device.
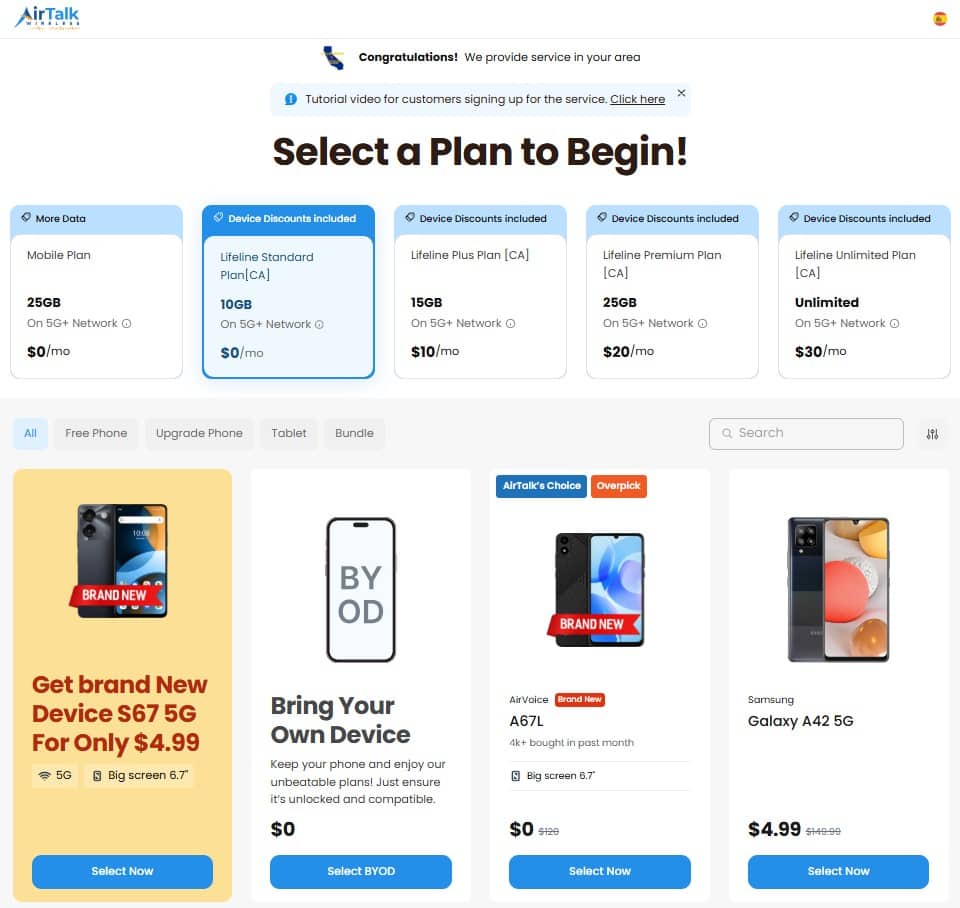
Step 4: Upload your documents (if needed)
Step 5: Submit your application for review.
In addition to Lifeline, there are other programs for which SNAP qualifies you, including Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) and the Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP). These programs can provide additional support to help you save money and access important services.

>>> Read more: How To Get A Free Tablet With EBT
Conclusion
If you want to learn more or need help navigating government assistance programs, our resources are available to guide you. Start exploring today to find the best options for you and your family’s needs.


